In this guide, I will walk you through exactly how to perform a complete SEO audit, step by step—without drowning in data or overcomplicating the process.
This is the same framework that helped me increase organic traffic by 40% for one of my clients in the furniture industry.
So, if your goal is to improve Google rankings and site performance, you’ll find this checklist packed with practical, actionable steps you can apply right away.
Run a Full Website Crawl
A full site crawl is the fastest way to collect technical and on-page data across your entire website.
A crawl helps you uncover issues related to:
- Crawlability and indexability
- Page speed and performance
- Internal linking structure
- Structured data
- On-page SEO elements
- And more
A crawl gives you a high-level diagnosis in one go.
How to Run a Crawl
One popular option is Screaming Frog.
It provides detailed insights into title tags, meta descriptions, images, broken links, and site architecture.
You can crawl up to 500 URLs for free, with paid plans available for larger sites.
Another excellent option is Semrush Site Audit, which goes beyond crawling and performs a full technical audit.
It checks for 100+ potential issues, including performance problems, internal linking gaps, and international SEO errors.
To start, enter your domain and click “Start Audit.”
You can customize crawl settings, limit pages, choose user agents, and even schedule recurring audits—helpful for catching issues before they impact rankings.
The Overview tab gives you a snapshot of your site’s health, including errors, warnings, and notices.
Review Your Organic Traffic
Since SEO is all about search visibility, the first thing you need to understand is how much traffic search engines are currently sending to your site.
Start by opening Google Analytics (GA4).
Navigate to:
Reports → Acquisition → Traffic acquisition
In the table, look for “Organic Search” under the default channel group.
Adjust the date range to analyze performance over a longer period so you can spot trends rather than short-term fluctuations.
Before moving forward, identify which pages generate the most clicks from Google.
You’ll find this data in Google Search Console under:
Performance → Search results → Pages
Knowing which pages perform well—and which ones underperform—helps you prioritize fixes during and after your audit.
If your organic traffic is flat or declining, don’t panic.
At this stage, you’re simply establishing benchmarks.
The entire purpose of this SEO audit is to improve performance from here.
Optimize Your Most Important Pages
On-page SEO still plays a major role in rankings. That said, you don’t need to optimize every page at once.
Instead, start by identifying your 5 highest-priority pages, such as:
- Pages targeting valuable keywords
- Pages that used to perform well but lost traffic
- Pages ranking just outside the top 5
If time is limited, focus on these essentials:
- Include your primary keyword in the title tag
- Use the keyword naturally in the first 100 words
- Add at least 5 relevant internal links
- Add at least 5 helpful external links
- Optimize images with descriptive filenames and alt text
You can monitor keyword movement using a tool like Semrush, SEranking, Ahref to see how optimizations affect rankings over time.
Optimize for UX Signals
User experience plays a critical role in modern SEO.
While Google has long avoided being explicit, evidence from algorithm updates and legal disclosures suggests user interaction signals help train ranking systems.
In simple terms: If users are happy, rankings tend to improve.
For example, we once found a page ranking between positions 10–15 because it didn’t match user intent. It focused on a single case study instead of providing clear, step-by-step guidance.
After rewriting the content to better answer the query—adding actionable steps, examples, and updated visuals—the page climbed to the top 5 results.
The lesson is clear: Optimize content for clarity, usefulness, and intent, not just keywords.
Strengthen Your Internal Linking
Internal linking is one of the most overlooked SEO tactics, yet it has a huge impact.
Make sure every page on your site has at least one internal link pointing to it. This prevents orphan pages, which are difficult for both users and search engines to find.
A good starting point is 3+ internal links per page, as long as they’re relevant and useful.
Strong internal linking also reduces crawl depth—the number of clicks it takes to reach a page from your homepage.
Ideally, important pages should be reachable within three clicks or fewer.
You can identify deep pages using the crawl depth report in Semrush Site Audit.
Optimize for Featured Snippets and AI Overviews
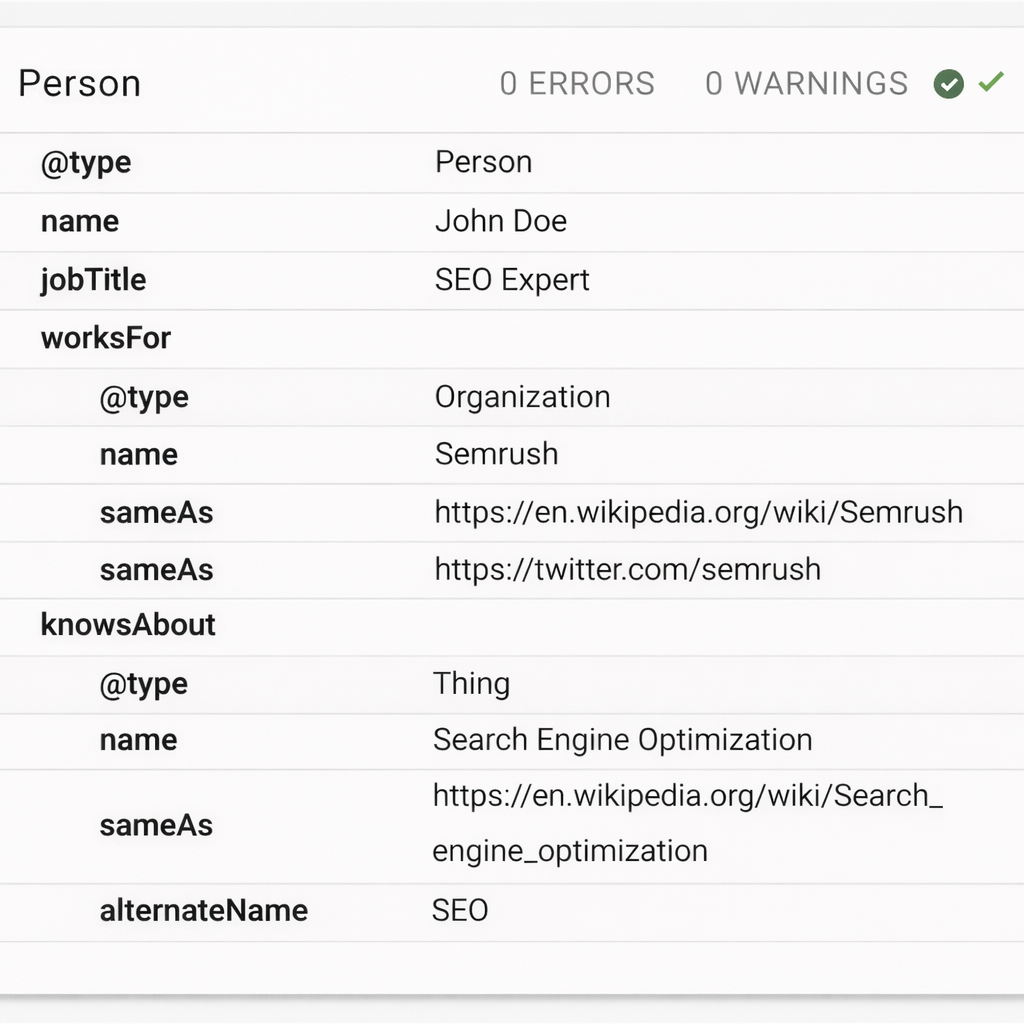
Featured snippets and AI-generated answers often appear above traditional search results, making them valuable visibility opportunities.
To optimize for them:
- Identify keywords that trigger snippets or AI summaries
- Add concise answers (40–60 words) under question-based headings
- Use clean formatting like lists, steps, and tables
- Strengthen E-E-A-T with author bios, references, and original insights
- Apply relevant schema (FAQ, HowTo, Q&A) where appropriate
- Ensure pages are crawlable, indexable, and mobile-friendly
Rather than chasing “position zero,” focus on making your content the clearest and most helpful answer available.
Strengthen Your E-E-A-T Signals (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust)
Strong SEO isn’t just about technical fixes — it’s also about credibility. Google wants to rank content created by people who demonstrate real experience, proven expertise, and trustworthiness.
To strengthen your E-E-A-T signals, make sure your key pages clearly show who created the content and why they’re qualified. Add author bios with relevant experience, link to reputable sources where appropriate, and include real examples, case studies, or first-hand insights that can’t be easily replicated.
Support trust with transparent business information, clear contact details, up-to-date content, and accurate claims. When users — and search engines — can confidently trust your content, your rankings are far more likely to hold up over time.
Check Page Rendering
After crawling, Google renders your page by executing JavaScript—just like a user’s browser.
If JavaScript issues prevent content from loading properly, Google may not see important elements like reviews, buttons, or interactive features.
Use Google Search Console → URL Inspection → View Tested Page to compare how Google renders your page versus how it should appear.
Tools like Semrush Site Audit can also flag JavaScript-related problems quickly.
Improve Site Speed (Core Web Vitals)
Page speed has been a ranking factor for years, and Google continues refining how it’s measured—most recently with INP.
Use PageSpeed Insights to identify issues, optimize HTML and images, and review Core Web Vitals metrics.
Compress images, reduce unnecessary scripts, and consider better hosting if performance remains slow.
Create 10x Better Content
To compete today, your content must offer significantly more value than what already exists.
Keep intros short, use scannable paragraphs, add clear subheadings, and support explanations with visuals and examples.


